

- Freepbx tutorial install#
- Freepbx tutorial driver#
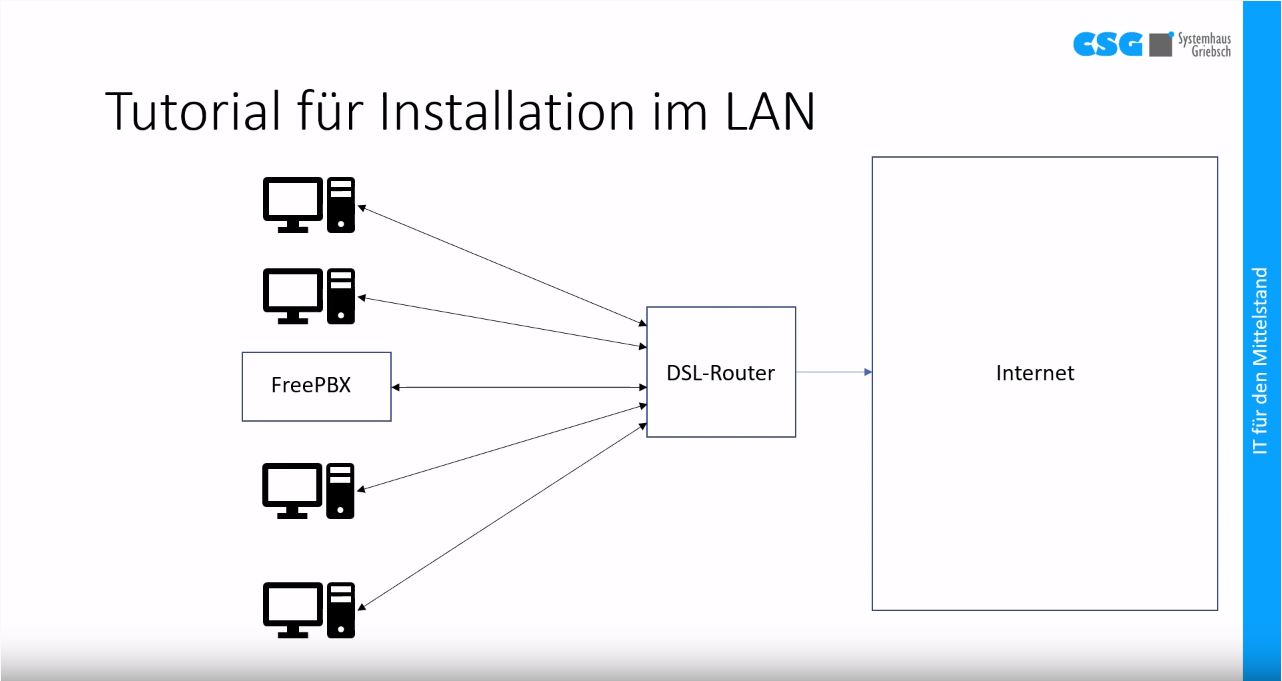
This may require firewall settings, NAT configuration, router changes for default address passing, and possibly a VPN to make the extensions “local” to your PBX.
You do not need a trunk to connect extensions, but you do need a clear network IP path to get from the phone to the server and back again. Freepbx tutorial driver#
SIP phones can connect to either, but they must be set up in the channel driver as Chan-SIP extensions or PJ-SIP extensions. This extension will also be used to receive incoming calls, monitor other extensions and transfer incoming calls to them. Freepbx tutorial install#
The port you access the phone system with (5060 or 5160) determines which channel driver you are using. Creating an account for VOP To install Voice Operator Panel (VOP) with FreePBX you need to create an extension that VOP will use to register to the FreePBX server. Youll need to assign your PBX a static IP address so that your phones will have a consistent internal IP address to use to contact it. This tutorial will help you to Install FreePBX 15 on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04/16.04 & Debian 10/9. You have added one or more PJSIP extensions to your FreePBX configuration, with appropriate routes for sending and receiving phone calls. There are a lot of things in this thread that confused me, so I’m going to make some suggestions that may or may not help you. When FreePBX is first installed, it is configured to obtain an IP Address using DHCP. FreePBX is a web-based open source GUI (graphical user interface) that controls and manages Asterisk (PBX). For this particular tutorial, we assume the following: You have configured your FreePBX so that it has a PJSIP trunk that is registering with one of the VoIP.ms POPs (Point of Presence). Normally, PJ-SIP is assigned to port 5060 and Chan-SIP (deprecated and no longer maintained) is on port 5160. PJ-SIP is SIP, just a different channel driver.








